In the ever-evolving landscape of modern electronics production, the significance of PCB printing cannot be overstated. As the backbone of electronic devices, printed circuit boards (PCBs) not only serve as the foundation for connecting various components but also play a critical role in the miniaturization and performance enhancement of technology. Renowned industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher in PCB technology, emphasizes, "The precision and efficiency of PCB printing are what allow us to meet the demands of advanced electronics."
This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of why PCB printing is essential in today's manufacturing processes. The advances in PCB printing techniques have enabled manufacturers to produce high-quality, reliable circuit boards rapidly and sustainably. This evolution is synonymous with the growth of modern electronics, where increasing functionality, reduced size, and enhanced reliability are paramount. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will uncover the critical elements that make PCB printing integral to technological innovation and how it drives the future of electronics production.

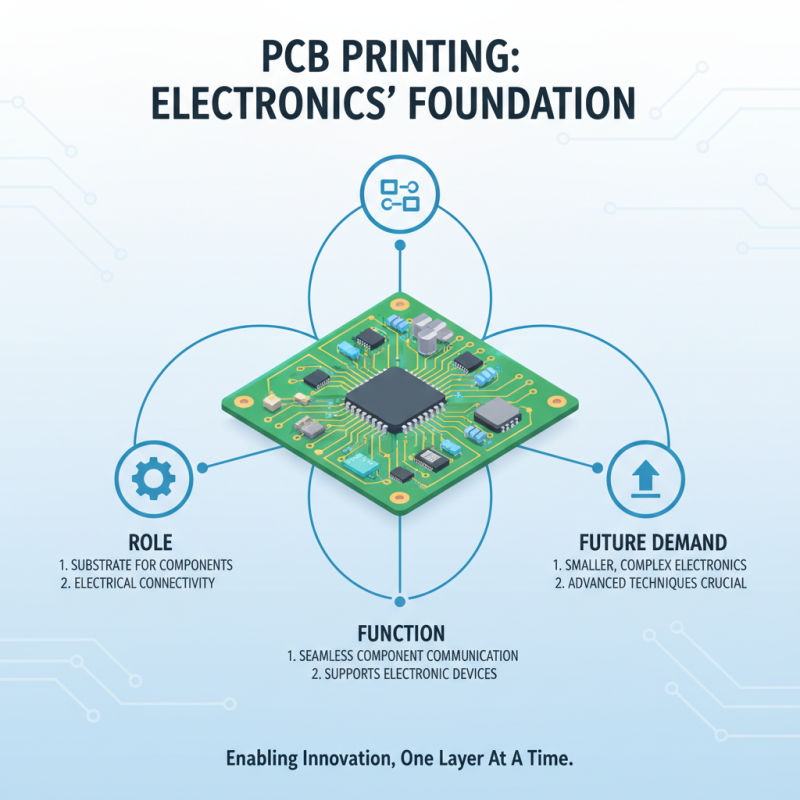
PCB printing plays a crucial role in the electronics manufacturing industry by providing a reliable and efficient way to create circuit boards that are foundational to various electronic devices. The printed circuit board (PCB) serves as a substrate to electrically connect and support electronic components, enabling seamless communication between them. As the demand for smaller, more complex electronics grows, the need for advanced PCB printing techniques becomes increasingly important to meet these challenges without compromising functionality.
Moreover, the precision required in PCB manufacturing is facilitated by modern printing technologies, which allow for high-resolution designs and intricate patterns that traditional methods cannot achieve. This capability not only supports the miniaturization of electronics but also enhances performance by reducing the space needed for connections. By incorporating advancements in materials and production techniques, PCB printing helps manufacturers achieve faster production times and improved quality control, ensuring that the end products are both reliable and cost-effective. Thus, PCB printing is not just a step in the manufacturing process; it is a pivotal element that drives innovation in the electronics industry.
The PCB printing process is a crucial step in modern electronics production, as it transforms conceptual designs into tangible circuit boards. This process typically begins with the design phase, where engineers use specialized software to create a detailed layout of the board, encompassing the arrangement of components and circuitry. Once the design is finalized, it is translated into a physical form through various printing techniques, including screen printing, inkjet printing, and direct imaging. Each technique has unique advantages, catering to different production scales and requirements.
Tip: When confirming your PCB design for printing, make sure to conduct thorough checks for clearance and spacing to avoid potential errors during production. Small oversights can lead to significant functional issues in electronic devices.
Post-printing, the boards undergo a series of processes such as etching, drilling, and plating, which further refine the board for its intended use. These processes ensure that the copper traces are accurately designed and that the circuits meet the necessary specifications. The quality of the printed PCB directly impacts the reliability and performance of the electronics, making each step of the printing process vital.
Tip: Always stay updated with the latest PCB manufacturing technologies. Advances in printing techniques can enhance efficiency and improve the quality of your electronics products, leading to greater customer satisfaction.
| Process | Description | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screen Printing | A method where ink is forced through a screen onto the board. | High-volume production, basic circuit designs. | Cost-effective for large batches, simple setup. |
| Offset Printing | Transferring ink from a plate to the board. | Complex graphic designs, prototyping. | High precision, excellent print quality. |
| Direct Printing | Printing directly onto the PCB from a digital file. | Rapid prototyping, short runs. | Fast turnaround, no need for screens or plates. |
| Laser Printing | Using laser technology to transfer images onto the PCB. | Small production runs, intricate designs. | High detail, minimal material waste. |
PCB printing is a cornerstone of modern electronics production, offering a multitude of advantages that enhance both the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing processes. One of the primary benefits of PCB printing is its ability to streamline the design and fabrication of complex electronic circuits. By using cutting-edge printing techniques, manufacturers can produce detailed and intricate designs with high precision, reducing the risk of errors that often arise in traditional methods. This not only accelerates the production timeline but also leads to more reliable final products.
Another significant advantage of PCB printing is cost-effectiveness. Unlike conventional methods that may require extensive tooling and setup, PCB printing tends to have lower initial costs and can accommodate smaller production runs. This flexibility allows manufacturers to swiftly adapt to market changes and customer preferences, making it easier to introduce new products. Additionally, advances in printing technology have enabled the use of novel materials and substrates, further expanding the possibilities for innovative electronic designs. Overall, the integration of PCB printing into modern electronics production significantly enhances both creativity and productivity.
PCB printing plays a crucial role in modern electronics production, utilizing a variety of key materials and technologies that enhance the efficiency and functionality of electronic devices. One of the primary materials used in PCB manufacturing is copper, which serves as the conductive pathway for electrical signals. The quality of copper plating directly affects the performance and reliability of PCBs, necessitating precise processes during fabrication. Additionally, substrate materials like FR-4, a composite of woven fiberglass and epoxy resin, contribute to the structural integrity and insulating properties of PCBs. These materials are chosen based on mechanical strength, thermal stability, and dielectric constant, ensuring optimal performance in different applications.
Technological advancements in PCB printing have optimized the manufacturing process, increasing precision and reducing production time. Techniques such as additive manufacturing and screen printing allow for intricate circuit designs and better space utilization on the board. Furthermore, surface mount technology (SMT) has revolutionized electronics assembly by enabling components to be mounted directly onto the PCB surface, facilitating smaller, more efficient designs. Innovations in soldering techniques, such as selective soldering and wave soldering, have also improved the reliability of connections on PCBs, making them more robust and capable of supporting the ever-growing complexity of modern electronic systems.
The future of PCB printing is poised to revolutionize the landscape of advanced electronics production. With the growing demand for miniaturization and high-performance devices, manufacturers are increasingly turning to innovative printing techniques that enhance the capabilities and efficiency of printed circuit boards. Technologies like additive manufacturing and 3D printing are allowing for more complex designs and multi-layered circuits, enabling the integration of components that were previously difficult to combine. This advancement not only streamlines the production process but also significantly reduces material waste, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices.
Moreover, the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is driving the need for flexible and adaptable PCB designs. Future trends indicate a shift towards flexible electronic circuits that can be integrated into a variety of surfaces and products, from wearables to smart home devices. Techniques such as roll-to-roll printing are becoming increasingly popular, allowing for high-volume production of flexible PCBs at lower costs. As these trends continue to evolve, PCB printing will play a crucial role in meeting the demands for high-speed connectivity, increased functionality, and design versatility in the next generation of electronic devices.