Choosing the right process for circuit board manufacturing is a critical decision that can significantly impact the performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of electronic devices. As technology continues to evolve, the complexity of circuit board designs increases, necessitating a careful evaluation of the various manufacturing techniques available. Each method, whether it be traditional methods like etching or advanced techniques such as additive manufacturing, offers unique advantages and challenges that must be considered based on specific project requirements.
In this context, factors such as production volume, material compatibility, and lead times play a vital role in determining the most suitable process. Understanding these parameters not only aids in optimizing production efficiency but also ensures that the final product meets stringent quality standards. By assessing these elements, manufacturers can align their circuit board manufacturing techniques with their operational goals, ultimately leading to enhanced product innovation and market competitiveness.
In conclusion, the choice of circuit board manufacturing techniques is pivotal for any project involving electronics. A comprehensive understanding of the various processes helps to make informed decisions that cater to both technical specifications and budget constraints, laying a strong foundation for successful product development in an increasingly competitive landscape.
When considering circuit board manufacturing techniques, it's crucial to understand the various methods available, as each comes with its own set of advantages and applications. The most common techniques include subtractive, additive, and hybrid processes.
Subtractive manufacturing involves etching copper layers on a substrate to create circuit pathways. This traditional method is widely used due to its reliability and cost-effectiveness for producing high volumes of boards. However, it may not be suitable for complex or high-density designs.
Additive manufacturing, on the other hand, is a more modern approach that builds up circuit designs layer by layer. This technique allows for intricate designs and often results in less waste material compared to subtractive methods. It's particularly beneficial for prototype development and low-volume production, where customization is key.
Hybrid techniques combine elements of both subtractive and additive processes, enabling manufacturers to leverage the strengths of each method to meet specific project requirements. Understanding these techniques helps manufacturers make informed decisions that align with their production goals and the demands of their projects.
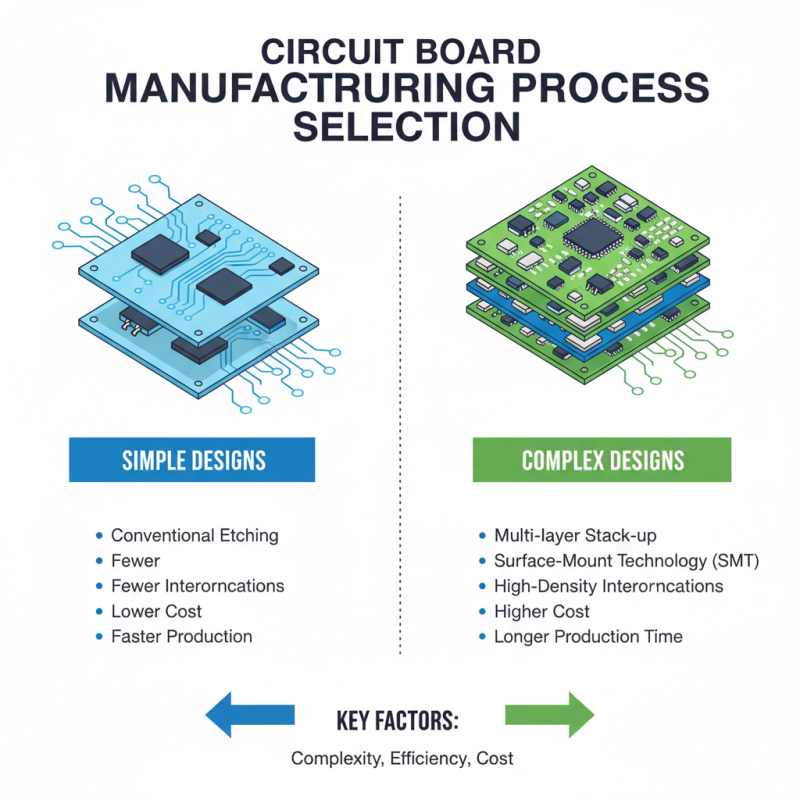
When choosing the right process for circuit board manufacturing, several key factors must be considered to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness. First and foremost, the complexity of the circuit design plays a crucial role. Simple designs may be efficiently produced using standard methods such as conventional etching. However, intricate designs that require high-density interconnections necessitate advanced techniques like multi-layer stack-up or surface-mount technology, which can increase production time and cost.
Another significant aspect is the material selection. Different materials can impact both the performance and durability of the final product. For instance, options like FR-4 or high-frequency materials are suited for specific applications such as telecommunications or automotive sectors. Manufacturers need to align their choice of materials with the end-use requirements to ensure that the circuit boards meet both operational standards and regulatory compliance. Additionally, flexibility in production volume is vital; companies must evaluate whether they require fast turnarounds for prototype runs or high-volume production, as this will dictate the feasibility of various manufacturing methods.
When choosing a process for circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, it's essential to conduct a comparative analysis of various production methods based on cost and efficiency. Traditional manufacturing techniques, such as through-hole technology, tend to be more labor-intensive and therefore can incur higher costs. However, this method excels in producing durable connections, particularly for components that require a robust mechanical bond. On the other hand, surface mount technology (SMT) provides a more automated production line, significantly reducing labor costs while increasing the overall efficiency of PCB assembly. The choice between these methods hinges on the specific requirements of the project, including the volume of production and the complexity of the circuit design.
Additionally, newer methods like additive manufacturing are gaining traction due to their potential for reducing material waste and improving design flexibility. While these methods may initially come with higher equipment costs, the long-term savings from decreased material usage and faster prototyping can make them a viable option for companies looking to innovate. Ultimately, the right production technique will depend on evaluating these factors—cost implications, efficiency of processes, and the scalability of production—to ensure that the selected method aligns with the overall goals of the project and the needs of the market.
Emerging technologies in circuit board fabrication are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, significantly impacting efficiency and precision. As industries increasingly demand miniaturized and complex electronic components, innovative techniques such as additive manufacturing and advanced automated processes are gaining traction. According to a recent market report from IPC, the global printed circuit board (PCB) market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.4% from 2022 to 2027, indicating robust demand for these advanced fabrication technologies.
One of the most promising developments is the use of 3D printing in PCB fabrication. This technology allows for greater design flexibility and faster prototyping, enabling engineers to streamline development processes. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence in manufacturing processes enhances quality control by identifying defects in real time, ensuring higher reliability of end products. Industry data highlights that implementing AI-driven quality assurance can reduce failure rates by up to 30%, providing substantial cost savings.
**Tips:** When considering the right process for circuit board manufacturing, assess the specific requirements of your project, including design complexity and production volume. It's essential to stay informed about emerging technologies to choose the method that can best enhance efficiency while meeting quality standards. Engage with specialized providers who can offer insights into the latest advancements and tailor solutions to your needs.
In the realm of PCB manufacturing, adhering to industry standards and implementing robust quality control measures are paramount for achieving excellence and reliability in circuit board production. Industry standards, such as IPC standards, provide essential guidelines that define the acceptable practices and performance metrics for PCB manufacturers. These standards address various aspects, including materials, processes, and final product testing, ensuring that circuit boards meet the required specifications for functionality and durability. By following these standards, manufacturers can avoid defects and reduce the likelihood of failures in electronic devices.
Quality control in PCB manufacturing plays a critical role in safeguarding performance and longevity. It encompasses a series of rigorous inspections and tests designed to evaluate every phase of production, from the selection of raw materials to the final assembly. Techniques such as automated optical inspection (AOI) and electrical testing are commonly employed to detect inconsistencies and guarantee that each board adheres to the established specifications. Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and training among staff can further enhance quality outcomes, ensuring that each circuit board not only meets industry standards but also exceeds customer expectations.